Extended Events can replace SQL Profiler, and it is more powerful with less performance impact than SQL Profiler. Extended Events has been introduced in SQL Server world from SQL2008, and in SQL2012, it has been integrated into SQL Server Management Studio(SSMS), see the pic below:
CREATE EVENT SESSION [system_health] ON SERVER
ADD EVENT sqlclr.clr_allocation_failure(
ACTION(package0.callstack,sqlserver.session_id)),
ADD EVENT sqlclr.clr_virtual_alloc_failure(
ACTION(package0.callstack,sqlserver.session_id)),
ADD EVENT sqlos.memory_broker_ring_buffer_recorded,
ADD EVENT sqlos.memory_node_oom_ring_buffer_recorded(
ACTION(package0.callstack,sqlserver.session_id,sqlserver.sql_text,sqlserver.tsql_stack)),
ADD EVENT sqlos.scheduler_monitor_deadlock_ring_buffer_recorded,
ADD EVENT sqlos.scheduler_monitor_non_yielding_iocp_ring_buffer_recorded,
ADD EVENT sqlos.scheduler_monitor_non_yielding_ring_buffer_recorded,
ADD EVENT sqlos.scheduler_monitor_non_yielding_rm_ring_buffer_recorded,
ADD EVENT sqlos.scheduler_monitor_stalled_dispatcher_ring_buffer_recorded,
ADD EVENT sqlos.scheduler_monitor_system_health_ring_buffer_recorded,
ADD EVENT sqlos.wait_info(
ACTION(package0.callstack,sqlserver.session_id,sqlserver.sql_text)
WHERE ([duration]>(15000) AND ([wait_type]>(31) AND ([wait_type]>(47) AND [wait_type]<(54) OR [wait_type]<(38) OR [wait_type]>(63) AND [wait_type]<(70) OR [wait_type]>(96) AND [wait_type]<(100) OR [wait_type]=(107) OR [wait_type]=(113) OR [wait_type]>(174) AND [wait_type]<(179) OR [wait_type]=(186) OR [wait_type]=(207) OR [wait_type]=(269) OR [wait_type]=(283) OR [wait_type]=(284)) OR [duration]>(30000) AND [wait_type]<(22)))),
ADD EVENT sqlos.wait_info_external(
ACTION(package0.callstack,sqlserver.session_id,sqlserver.sql_text)
WHERE ([duration]>(5000) AND ([wait_type]>(365) AND [wait_type]<(372) OR [wait_type]>(372) AND [wait_type]<(377) OR [wait_type]>(377) AND [wait_type]<(383) OR [wait_type]>(420) AND [wait_type]<(424) OR [wait_type]>(426) AND [wait_type]<(432) OR [wait_type]>(432) AND [wait_type]<(435) OR [duration]>(45000) AND ([wait_type]>(382) AND [wait_type]<(386) OR [wait_type]>(423) AND [wait_type]<(427) OR [wait_type]>(434) AND [wait_type]<(437) OR [wait_type]>(442) AND [wait_type]<(451) OR [wait_type]>(451) AND [wait_type]<(473) OR [wait_type]>(484) AND [wait_type]<(499) OR [wait_type]=(365) OR [wait_type]=(372) OR [wait_type]=(377) OR [wait_type]=(387) OR [wait_type]=(432) OR [wait_type]=(502))))),
ADD EVENT sqlserver.connectivity_ring_buffer_recorded(SET collect_call_stack=(1)),
ADD EVENT sqlserver.error_reported(
ACTION(package0.callstack,sqlserver.database_id,sqlserver.session_id,sqlserver.sql_text,sqlserver.tsql_stack)
WHERE ([severity]>=(20) OR ([error_number]=(17803) OR [error_number]=(701) OR [error_number]=(802) OR [error_number]=(8645) OR [error_number]=(8651) OR [error_number]=(8657) OR [error_number]=(8902)))),
ADD EVENT sqlserver.security_error_ring_buffer_recorded(SET collect_call_stack=(1)),
ADD EVENT sqlserver.sp_server_diagnostics_component_result(SET collect_data=(1)
WHERE ([sqlserver].[is_system]=(1) AND [component]<>(4))),
ADD EVENT sqlserver.xml_deadlock_report
ADD TARGET package0.event_file(SET filename=N'system_health.xel',max_file_size=(5),max_rollover_files=(4)),
ADD TARGET package0.ring_buffer(SET max_events_limit=(5000),max_memory=(4096))
WITH (MAX_MEMORY=4096 KB,EVENT_RETENTION_MODE=ALLOW_SINGLE_EVENT_LOSS,MAX_DISPATCH_LATENCY=120 SECONDS,MAX_EVENT_SIZE=0 KB,MEMORY_PARTITION_MODE=NONE,TRACK_CAUSALITY=OFF,STARTUP_STATE=OFF)
GO
So "system_health" will monitor the deadlock event by default. let's try the script below to generate deadlock scenario
====================================================
--create table
create table a1(a int)
create table b1(b int)
insert into a1 values(1)
insert into b1 values(1)
--run in first session
select @@SPID
begin tran
update a1 set a=2
update b1 set b=2
--run in second session
select @@SPID
begin tran
update b1 set b=2
update a1 set a=2
====================================================
Congrat, you got deadlock and saw the error below
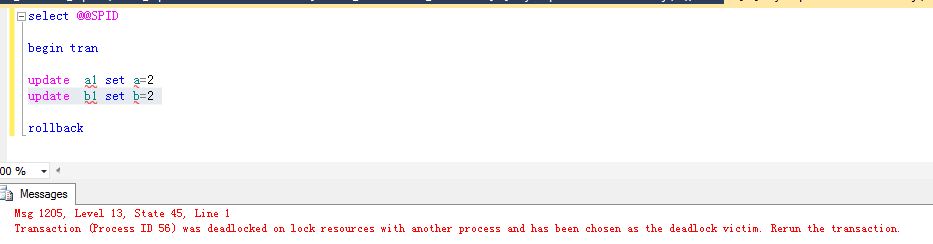
Go back to SSMS,
double click the "package0.event_file" under "system_health", you can review all the event just like below:
Double Click "Value" to check the deadlock detail, here you can find the process and resource info for the deadlock
==============================================
<deadlock>
<victim-list><victimProcess id="process2ed016558" />
</victim-list>
<process-list>
<process id="process2ed016558" taskpriority="0" logused="248" waitresource="RID: 6:1:169:0" waittime="3029" ownerId="54473" transactionname="user_transaction" lasttranstarted="2012-08-12T18:59:15.827" XDES="0x2f8252d28" lockMode="U" schedulerid="3" kpid="4852" status="suspended" spid="56" sbid="0" ecid="0" priority="0" trancount="2" lastbatchstarted="2012-08-12T18:59:23.397" lastbatchcompleted="2012-08-12T18:59:15.830" lastattention="1900-01-01T00:00:00.830" clientapp="Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio - Query" hostname="V-XUJ1230" hostpid="5688" loginname="FAREAST\v-xuj" isolationlevel="read committed (2)" xactid="54473" currentdb="6" lockTimeout="4294967295" clientoption1="671090784" clientoption2="390200">
<executionStack>
<frame procname="adhoc" line="1" stmtstart="16" sqlhandle="0x020000006377082c50d69d2e5f1de789330d2a1e2eda81960000000000000000000000000000000000000000">
UPDATE [b1] set [b] = @1 </frame>
<frame procname="adhoc" line="1" sqlhandle="0x0200000055304113cb84f9da843e5bdb59f3c2ace4f8aadd0000000000000000000000000000000000000000">
update b1 set b=2 </frame>
</executionStack>
<inputbuf>
update b1 set b=2
</inputbuf>
</process>
<process id="process2ed0170c8" taskpriority="0" logused="248" waitresource="RID: 6:1:166:0" waittime="6233" ownerId="54474" transactionname="user_transaction" lasttranstarted="2012-08-12T18:59:18.503" XDES="0x2f82523a8" lockMode="U" schedulerid="3" kpid="1456" status="suspended" spid="52" sbid="0" ecid="0" priority="0" trancount="2" lastbatchstarted="2012-08-12T18:59:20.210" lastbatchcompleted="2012-08-12T18:59:18.503" lastattention="1900-01-01T00:00:00.503" clientapp="Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio - Query" hostname="V-XUJ1230" hostpid="5688" loginname="FAREAST\v-xuj" isolationlevel="read committed (2)" xactid="54474" currentdb="6" lockTimeout="4294967295" clientoption1="671090784" clientoption2="390200">
<executionStack>
<frame procname="adhoc" line="1" stmtstart="16" sqlhandle="0x020000005cdb030dd161d461be83dc620591979030bbf17f0000000000000000000000000000000000000000">
UPDATE [a1] set [a] = @1 </frame>
<frame procname="adhoc" line="1" sqlhandle="0x020000008278b7001a4bf6c0edd6eb92e71651f531b4b9da0000000000000000000000000000000000000000">
update a1 set a=2 </frame>
</executionStack>
<inputbuf>
update a1 set a=2
</inputbuf>
</process>
</process-list>
<resource-list>
<ridlock fileid="1" pageid="169" dbid="6" objectname="CDBTEST.dbo.b1" id="lock2f4b46480" mode="X" associatedObjectId="72057594039107584">
<owner-list>
<owner id="process2ed0170c8" mode="X" />
</owner-list>
<waiter-list>
<waiter id="process2ed016558" mode="U" requestType="wait" />
</waiter-list>
</ridlock>
<ridlock fileid="1" pageid="166" dbid="6" objectname="CDBTEST.dbo.a1" id="lock2f4b49180" mode="X" associatedObjectId="72057594039042048">
<owner-list>
<owner id="process2ed016558" mode="X" />
</owner-list>
<waiter-list>
<waiter id="process2ed0170c8" mode="U" requestType="wait" />
</waiter-list>
</ridlock>
</resource-list>
</deadlock>
==============================================
or you can click the "Deadlock" TAB to see the diagram.



Did you know that that you can make money by locking special areas of your blog or website?
ReplyDeleteSimply join AdWorkMedia and implement their Content Locking plug-in.